When most people think of 3D printing, they think of the technology industry, but its remarkable adaptability is generally underestimated in sectors other than technology. Looking back at the history of 3D printing in healthcare confirms that 3D printing is not limited to the technological industry. The earliest application of 3D printing in medical sciences was for customized prostheses and dental implants in the 1990s. Eventually, the advancement of 3D printing technology has led us to doctors producing completely functional organs in the human body.
The 3D printing industry in healthcare is expected to grow at a staggering 22.5% CAGR over the next ten years, with a beginning value of USD 2 billion. Yes, you read that right.
But before we get into the details of the application of 3D printing in medical technology, let’s have a look at the 3D printing process itself.
3D printing in Healthcare
The advent of 3D printing has caused a paradigm shift in the healthcare industry. An estimated 20 million dollars will be spent on 3D printing globally by the end of this decade, with the healthcare industry spending the majority of that amount on the demands of an aging population. A growing number of medical professionals and providers are using 3D printing technology to better understand a patient’s anatomy without resorting to invasive procedures that increases the chance of injuring the patient. In addition, 3D printing technology dramatically cuts down on the amount of time needed to do surgeries and other medical treatments.
The application of 3D printing technology in healthcare has the potential to aid residents in war-torn nations or help repair some of the damage left behind by natural calamities. The development of prostheses at a cheap cost and, more critically, faster production and their timely provision can help limit the harm done to the individual.
Beyond manufacturing prostheses, 3D technology has broad applications in the healthcare sector. Here are some of the most captivating 3D printing uses in healthcare:
Applications of 3D Printing in Healthcare
1. Anatomical Replicas

Regarding the application of 3D printing in medical treatment, the primary focus has been manufacturing surgical instruments and other implants. However, now, the emphasis has evolved to utilizing 3D technologies to fabricate the anatomy (replica) of the patient. This allows doctors to have a better look into the patient’s condition without intrusive medical treatments. The anatomical replica of the patient created by 3D printing technology can be so perfect that doctors can explain the treatment plan and sometimes even aid in visualizing certain surgical techniques.
A replica of the patient anatomy structure created can help the doctor exactly size the medial instruments needed for the surgery. Furthermore, the replica can help the surgeon communicate the surgical stages to their colleagues and offer a better knowledge of the treatment plan to the patient’s family.
To help minimize the inherent risks and expenditures that generally accompany a surgery, patient-unique 3D models are created for surgeons to understand the surgical procedure clearly, even down to the touch and feel of the patient’s distinguishing components, before the surgery.
2. Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine
3D printing can be employed to generate functioning tissue and organs for transplant. By application of 3D technology in healthcare, such as bioprinting, to create growth-directed structures, one may control the growth of cells toward forming functional tissues. Additionally, it is employed in tissue model research, pharmaceutical toxicology testing, and drug screening.
Tissue engineering examples include generating breast tissues and reconstructing breasts for breast implantation in breast cancer survivors. Another possibility is to cure hair loss by rebuilding hair follicles using LIFT technology and regenerating hair on the patient scalp.
3. Customized Surgical Tools

Surgical instruments are required for surgeons to effectively perform an operation. Previously, surgical instruments were composed of titanium and aluminum, and their sizes were fairly standard. Application 3D printing in medical instruments allows clinicians to create surgical equipment that is perfect for the patient’s specific anatomy. Restorative treatments such as screws, plates, and implants can be inserted with extreme accuracy, lowering the chance of complications post-surgery. FDM technology in 3D printing, for example, is well suited for creating low-cost, high-efficiency surgical equipment.
4. Prosthetics and Implants
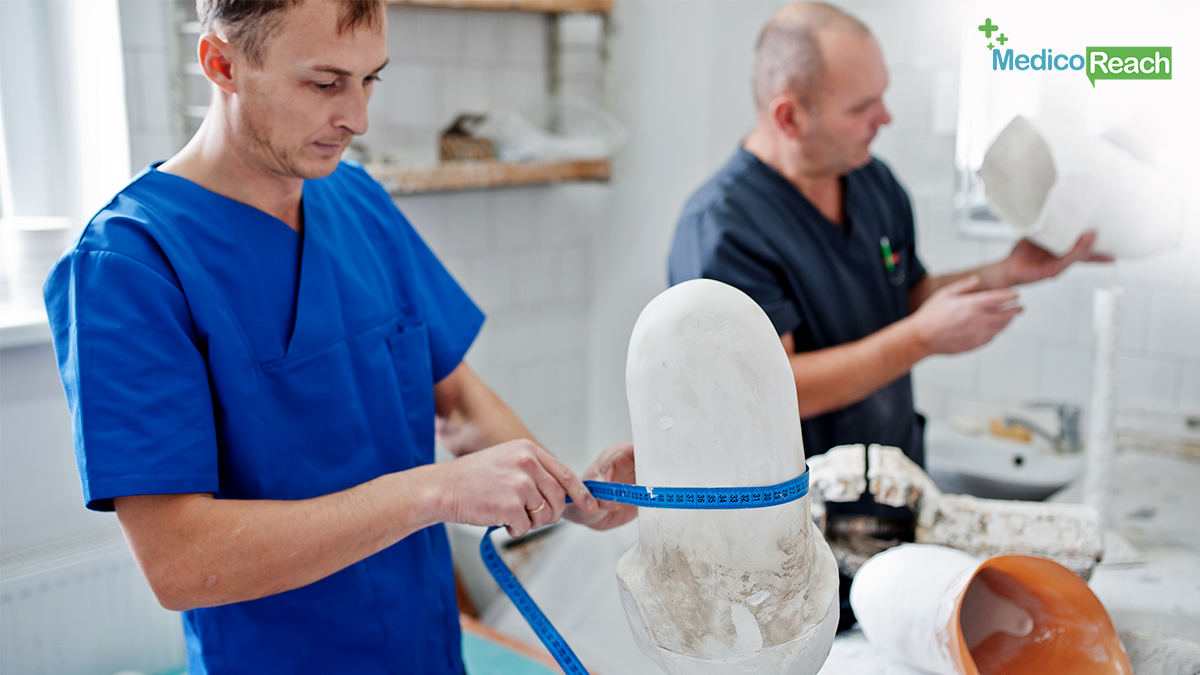

Around 100 million individuals use prosthetic limbs worldwide, and nearly 200 000 amputations are done in the United States alone each year. Replacement of arms and legs, or any other type of altercation is a pricey affair and can take a long time to curate because it must be tailored according to the individual’s specific anatomy. Not only has 3D printing revolutionized the world of prosthetics with exact modifications, it has also been shown to be cost-effective and efficient in producing prostheses that fit well with the individual’s unique anatomy.
5. Synthetic Organs
While the world has previously witnessed knee replacement and kidney transplant, which was nothing less than a miracle in itself, the idea of curating a human organ may still appear impossible to a layman. But it’s true: 3D printing can regenerate organs using the patient’s cells. This is nothing short of a medical breakthrough, as it can dramatically reduce the number of deaths caused by organ failure while also lowering the risks of using lifelong immunosuppressing medications, which are unavoidable in organ transplant surgery.
Conclusion
Besides the five uses stated above, 3D printing has many additional applications in healthcare. However, we feel that these are the five most significant developments brought about by the application of 3D printing in the medical field. As time passes, some of the specialist sectors in 3D printing will be made available to many medical institutions, and widespread adoption of the technology will result in more innovative applications of 3D printing in the medical profession to improve people’s lives.
But for now, it is safe to say that application of 3D printing is nothing less than a boon to humanity.